NewPath Learning Science Six Kingdoms of Life Visual Learning Guide Set, Grade 5-9
Every living creature on Earth belongs to a kingdom.There are countless organisms in the world and the scientific classification system was put in place to group together species that share common characteristics.
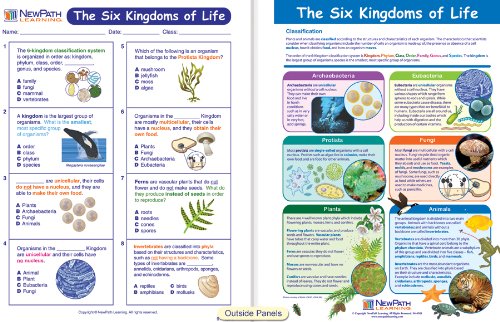
This classification system is rooted in the work of Carolus Linnaeus, who is known as the father of modern taxonomy. The scientific classification system in biology consists of seven different groups or rankings. These rankings include kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species.
When Linnaeus developed his system of classification, there were only two kingdoms,Plants and Animals. But the use of the microscope led to the discovery of new organisms and the identification of differences in cells. A two-kingdom system was no longer useful.
Today the system of classification includes six kingdoms.
The Six Kingdoms
Kingdom is the highest rank used in the biological taxonomy of all organisms. There are 6 kingdoms in taxonomy. Every living thing comes under one of these 6 kingdoms. The six kingdoms are Eubacteria, Archae, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia.
1.Eubacteria Kingdom

Bioprospects of Coastal Eubacteria: Ecosystems of Goa
The Eubacteria, also called just “bacteria,” are one of the three main domains of life, along with the Archaea and the Eukarya.
Eubacteria are prokaryotic, meaning their cells do not have defined, membrane-limited nuclei. As a group they display an impressive range of biochemical diversity, and their numerous members are found in every habitat on Earth.
Eubacteria are responsible for many human diseases, but also help maintain health and form vital parts of all of Earth’s ecosystems.
2.Archaea Kingdom

The archaea have ancient origin, just like the bacteria, but they are somewhat more advanced in certain features. A chief example of these features is that the circular DNA molecule is associated with DNA binding proteins.
Bacteria as you recall lack DNA binding proteins. So archaea are somewhere between bacteria and eukaryotes in this regard. These organisms have had a long time to evolve and diversify into cells with a wide range of forms and functions.
3.Protista Kingdom

All living organisms can be broadly divided into two groups — prokaryotes and eukaryotes — which are distinguished by the relative complexity of their cells. In contrast to prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells are highly organized. Bacteria and archaea are prokaryotes, while all other living organisms — protists, plants, animals and fungi — are eukaryotes.
Kingdom Protista is a diverse group of eukaryotic organisms. Protists are unicellular, some are colonial or multicellular, they do not have specialized tissue organization. The simple cellular organization distinguishes the protists from other eukaryotes. The cell body of the protists contain have a nucleus which is well defined and membrane bound organelles. Some have flagella or cilia for locomotion. Reproduction in protists is both asexual and sexual. They live in any environment that contains water.
All single celled organisms are placed under the Kingdom Protista. The term Protista was first used by Ernst Haeckel in the year 1886. This kingdom forms a link between other kingdoms of plants, animals and fungi. Protists represent an important step in early evolution. The first protists evolved probably 1.7 billion years ago. Members of Protista are primarily aquatic in nature. It is a very large group comprising of at least 16 phyla. Many protists like algae are the primary producers in the aquatic ecosystem, some protists are responsible for serious human diseases like malaria and sleeping sickness.
4.Fungi Kingdom

Fungi are important organisms that belong to their own kingdom, completely separate from plants and animals. A hugely diverse group of great economic importance, fungi remain vastly under-studied compared to plants.
It is estimated that there may be anything from 700,000 to 5 million species of fungi in the world. Even using the most widely cited estimate of 1.5 million, this makes fungi more than six times as diverse as flowering plants. Yet only about 100,000 species have so far been described.
Fungi show a great diversity in morphology and habitat. Fungi are heterotrophic organisms, they obtain their nutrients by absorption. The cell wall of fungi are mostly made up of carbohydrate chitin, while the cell wall in plants is made of cellulose. The carbohydrates stored in fungi is in the form of glycogen.
5.Plantae Kingdom

Virtually all other living creatures depend on plants to survive. Through photosynthesis, plants convert energy from sunlight into food stored as carbohydrates. Because animals cannot get energy directly from the sun, they must eat plants (or other animals that have had a vegetarian meal) to survive. Plants also provide the oxygen humans and animals breathe, because plants use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis and release oxygen into the atmosphere.
The kingdom Plantae includes organisms that range in size from a tiny moss to a giant tree. Despite this enormous variation, all plants are multicellular and eukaryotic (i.e., each cell possesses a membrane-bound nucleus that contains the chromosomes).
They generally possess pigments (chlorophylls a and b and carotenoids), which play a central role in converting the energy of sunlight into chemical energy by means of photosynthesis.
Most plants, therefore, are independent in their nutritional needs (autotrophic) and store their excess food in the form of macromolecules of starch. The relatively few plants that are not autotrophic have lost pigments and are dependent on other organisms for nutrients.
6.Animalia Kingdom

(24×36) Laminated Animal Kingdom 2 Educational Science Chart Poster
The word ‘animal’ is derived from the Latin word animalis which means ‘having breath’. The Kingdom Animalia is characterized by eukaryotic and heterotrophic organisms.
They are multicellular and lack cell wall. They depend directly or indirectly on plants for their food. Food is ingested and digested in their internal cavity and food reserves are stored as glycogen or fat. Nutrition is by ingestion of food.
Animals range in size from no more than a few cells to organisms weighing many tons, such as blue whales and giant squid.
By far most species of animals are insects, with groups such as mollusks, crustaceans, and nematodes also being especially diverse.
By this measure our own group, the vertebrates, is relatively inconsequential from a diversity perspective.

Mankind’s love for nature is perhaps one of the greatest mysteries of life, one that even evolutionary biologists are hard-pressed to explain.
This attraction is so strong that in the lap of Mother Nature, our minds immediately become calm and peaceful. We leave behind our trifling worries and mundane pursuits and are subconsciously drawn back to the wonders of nature.
When we think of beauty in nature, we might most immediately think of things that dazzle the senses – the prominence of a mountain, the expanse of the sea, the unfolding of the life of a flower.
Nature can reveal its beauty in all places and at all times to the eye that knows how to look for it.
There is so very much beauty all around us to see, touch, and hear. Nature is so miraculous because it is always changing. No matter how many times you look at something, it is always different.
Nature can bring a lot of beauty into our lives. Nature has a way of affecting our moods and it can force us to change our plans.
Nature is responsible for the sun, clouds, rain, and snow. When it is sunny and bright outside, we feel cheerful inside. When it is cloudy and rainy, we often feel gloomy.
Learning to become more aware of nature can truly have a good effect on our lives in the way we look at things and in the way we feel about ourselves.

Animal Charity Christmas Cards SELECTION PACK (12) British Animals World Wildlife and Nature WWF
Not only does direct exposure to nature increase happiness, but simply imagining yourself outdoors or recalling previous outdoor excursions has been shown to increase serotonin levels, thus boosting mood, decreasing exhaustion and improving overall health.
Nature is something within which we flourish, so having it be more a part of our lives is critical, especially when we live and work in built environments.
For people suffering from physical illness or mental health disorders, such as depression and anxiety, interacting with nature can help people control their symptoms or even recover, alongside conventional medication.
Nature isn’t just a nice thing to have – although it has a huge value in itself – it’s fundamentally important for our health, wellbeing and happiness!
Our culture teaches us that we never have enough. We strive to make more money, buy more things, eat more delicious food.
In contrast, eco systems embody harmony and balance. Trees grow to a height that reflects the nutrients and water immediately available. Squirrels store the right amount of food to get them through the winter.
Quietly witnessing this balance and harmony is like salve in the wound of overconsumption.
Spending time in the mountains or at the seaside helps us regain our focus and our capacity for innovation-time in the natural world restores attention and boosts creativity.
Jumpstart your love affair with nature by viewing this website. Check out the amazing natural wonders from around the world or closer to home!
If you have any information,questions, or feedback you would like to include in this webpage.
Please email momo19@naturekingdoms.com or leave your comments below.